使用树莓派的一些记录
网络 WiFi 问题
使用的 Zero W,没有网口。所以在不使用图形界面的时候,需要在命令行配置网络
1 | vim /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf |
ssid 是 WiFi 名称,psk 是密码,priority 是优先级,数字越大优先级越高。有些低版本的树莓派,只能连接 2.4G 的 Wifi。
1 | country=US |
WiFi 重启命令 1
ip link set wlan0 down && ip link set wlan up
fbterm 字体问题
1 | vim ~/.fbtermrc |
1 | font-names=mono |
https://bbs.deepin.org/post/230435
获取小米温湿度计的数据
需求
小米温湿度计用米家连接速度慢,且获取间隔为 1 小时一次,感觉有点慢,想要手动保存这些数据。
本来是想使用 HomeAssistant 来完成的,但发现 Python 版本要求 3.8 以上,而树莓派上的 Python 版本是 3.7。且就这一个设备,感觉没必要那么复杂。
好在已经有成熟的开源项目实现这一功能,https://github.com/JsBergbau/MiTemperature2。使用起来也很简单
准备
安装蓝牙驱动
1 | # 可以先输入 bluetoothctl 看看是否可以进入蓝牙交互界面,如果可以则无需安装 |
python 安装依赖 1
pip3 install bluepy
获取设备信息
1 | # 进入蓝牙交互界面 |
会持续扫描附近蓝牙设备,需要关注一个叫做 LYWSD03MMC 的设备(在设备后面有型号),这个就是小米温湿度计。
1 | ... |
记录这个设备的 MAC 地址,退出蓝牙交互界面
1 | exit |
实现
原来的代码过于复杂,还涉及一些其他的功能。核心功能是,获取温湿度信息即可。因此,我对代码进行了简化。在外面套一个定时任务即可。
把 MAC 地址写到下面的脚本中,然后运行脚本,就可以获取到温湿度信息了。
每 10 分钟获取一次温湿度信息,保存到 temp.log
文件中。如果每次获取失败次数超过 5 次,则退出程序。
1 | */10 * * * * cd /root/MiTemperature2 && /usr/bin/python3 mi_temp.py >> /root/MiTemperature2/temp.log |
下面的脚本可以获取树莓派本身的温度信息,保存到 temp.log
文件中。可以进行对比 1
2
echo `date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M"` `vcgencmd measure_temp` >> /home/pi/temp_save/temp.log
参考
[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/blueberry-mint/p/16575252.html
[2] https://github.com/JsBergbau/MiTemperature2
Notion 日历和苹果日历联动
需求描述
Notion 作为一个强大的笔记软件,吸引笔者使用的点在于跨平台,功能齐全。因此,在将 Notion 作为笔记软件使用的同时,也可以将其作为 TODO 事项管理软件使用。但是,移动端的 Notion 并没有实用的小组件视图。因此,结合之前的文章想到用 ics 文件来管理 Notion 的 TODO 事项。
数据获取
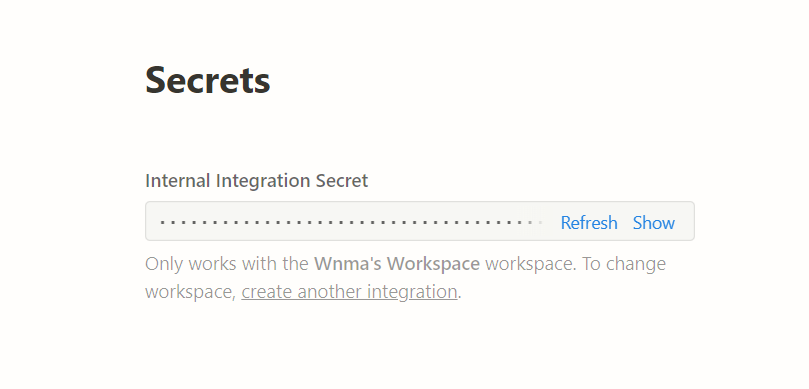
Notion 支持以 API 的方式获取 Page 的信息,尤其是当 Page 中主要以表格形式展示时,甚至可以用一系列过滤条件。首先,需要创建一个工具,以能够用 API 的方式获取 Notion 中的 Page 信息。https://www.notion.so/my-integrations,创建过程很简单,主要保存下 Secrets 即可。
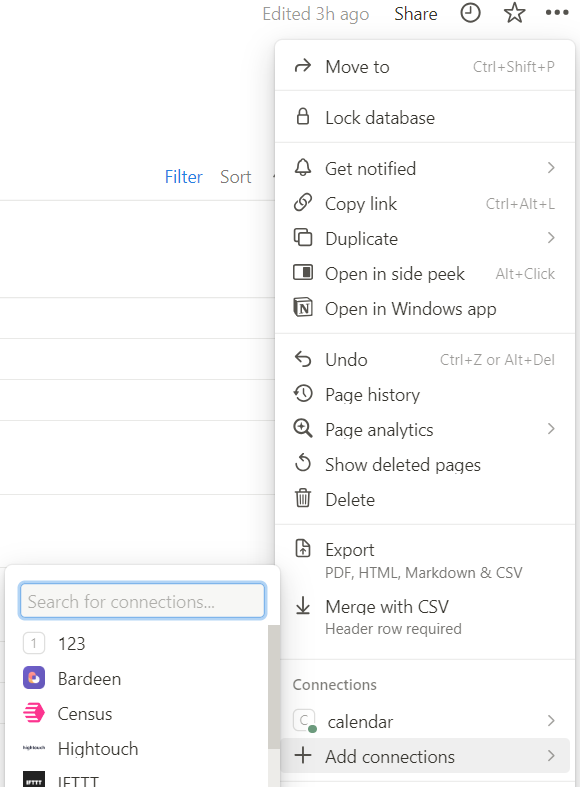
创建完成后,就可以在 Notion 的 Page 中 Add connections,如下图所示,可以把刚刚创建的工具,添加进来。比如这里是 123。
同时,保存 Page 页面的 url,比如 https://www.notion.so/AAA,访问页面时的 url,AAA 就是 dataset_id。至此,有两个信息,一个是 Secrets,一个是 dataset_id。将其粘贴至下面的 Python 代码中。
Python 的示例代码如下:
1 | import requests |
至此,Page 上的信息已经存到了 data_lst 中。
ics 文件生成
接下来,就是生成 ics 文件的生成。ics 文件的格式需要日程标题
summary、日程描述
description(可为空)、开始时间
dtstart、结束时间 dtend。
1 | from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone |
ics 部署
将生成的 ics 文件部署到服务器上,以便于服务器定期更新日程信息。同时,苹果可以订阅该 ics,以更新日程信息。
对于 tailscale 这一点而言,非常简单,只需要在服务器上运行如下命令即可。否则,需要使用域名 + nginx + https,这样才能将 ics 文件暴露出去,且苹果只接受 https 的 ics 文件。
1 | tailscale funnel --bg https+insecure://localhost --set-path /ics /data/my.ics |
另外,需要在服务器上,设置一个定时任务,定时运行上面的 python 脚本,以更新 notion 上的日程信息至 ics,最后苹果手机再接收到 ics 文件对日历进行更新。
苹果手机的订阅步骤如下:
设置 -> 日历 -> 账户 -> 添加账户 -> 其他 -> 添加已订阅的日历 -> 输入 ics 文件的 url 即可(比如这里应该是 https://A/ics)。这样就完成了所有的设置